Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
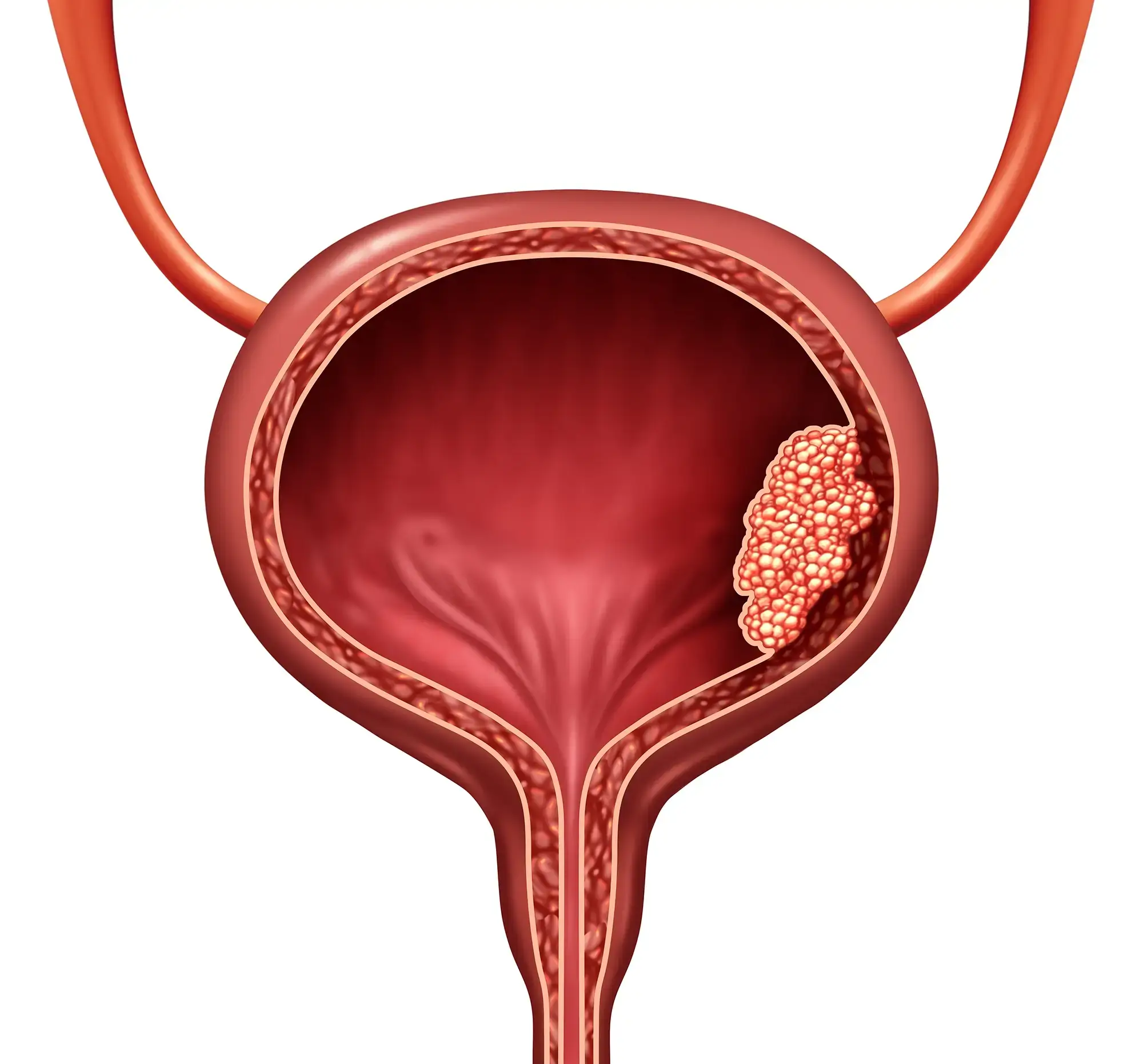
Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT) is a surgical procedure commonly used to diagnose and treat bladder tumors. It involves the removal of abnormal growths, such as tumors, from the inside lining of the bladder.
Below are an overview of what patients can expect during a transurethral resection of bladder tumor:
Preoperative Preparation:
- Before the surgery, patients may undergo various preoperative assessments, including blood tests and imaging studies.
- The healthcare team will provide instructions on fasting and medications, and patients may need to discontinue certain medications before the procedure.
Anesthesia:
- TURBT is typically performed under general anesthesia.
- General anesthesia induces a state of unconsciousness.
Cystoscopy and Resection:
- A resectoscope, a thin tube with a light and camera, is inserted through the urethra and into the bladder.
- Using a wired loop via the resectoscope, the surgeon uses the resectoscope to cut away or burn the tumor tissue.
- The removed tissue is sent to the laboratory for analysis to determine if cancer is present and to identify the type and grade of the tumor.
Hemostasis and Bladder Inspection:
- After removing the tumor, the surgeon ensures that any bleeding is controlled.
- The interior of the bladder is carefully inspected to identify any remaining tumors or abnormalities.
Postoperative Catheterization:
- In some cases, the urologist may perform additional procedures during cystoscopy.
- The catheter may be connected to a drainage bag and is usually removed within a day or two after the procedure.
Recovery and Hospital Stay:
- Most patients can expect a same day discharge.
- Recovery time varies, but patients may experience some discomfort, urinary urgency, or blood in the urine initially.
Follow-Up and Pathology Results:
- Patients will have follow-up appointments to discuss the results of the pathology report and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
- Depending on the findings, additional treatments such as intravesical therapy or further surgeries may be recommended.
