Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
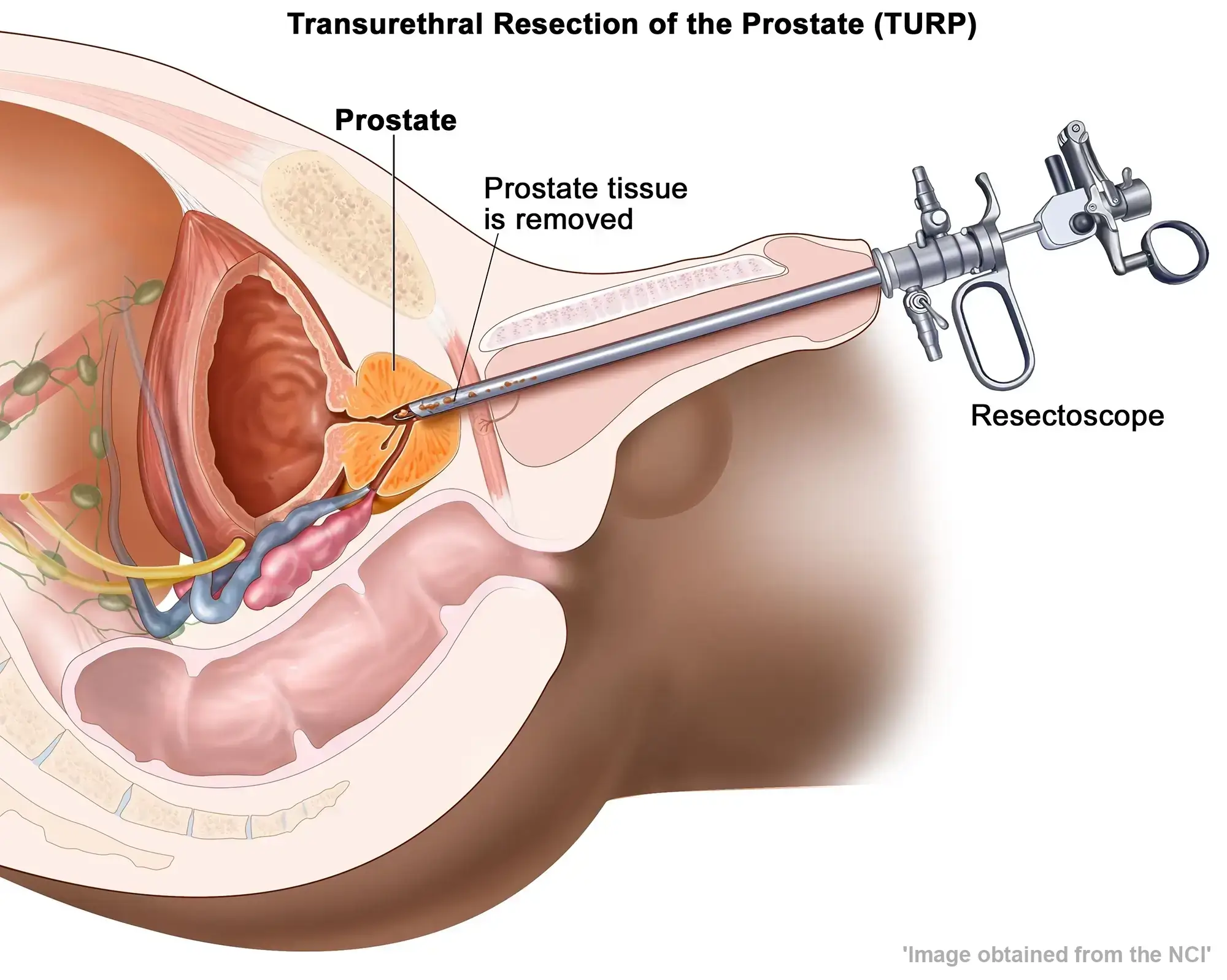
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure commonly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that can cause urinary symptoms.
Below are an overview of what patients can expect during a transurethral resection of the prostate:
Preoperative Preparation:
- Before the surgery, patients may undergo preoperative assessments, including blood tests, imaging studies, and a physical examination.
- The healthcare team will provide instructions on fasting, medications, and other preoperative preparations.
Anesthesia:
- TURBT is typically performed under general anesthesia.
- General anesthesia induces a state of unconsciousness.
Cystoscopy and Resection:
- A resectoscope, a thin tube with a light and camera, is inserted through the urethra and into the bladder.
- Using a wired loop via the resectoscope, the surgeon uses the resectoscope to cut away or burn the tumor tissue.
- The removed tissue is sent to the laboratory for analysis to determine if cancer is present and to identify the type and grade of the tumor.
Removal of Prostate Tissue:
- The surgeon carefully removes small pieces of the prostate tissue, creating a channel for improved urine flow.
- The surgeon also ensures that any bleeding is controlled to minimize the risk of complications.
Irrigation and Hemostasis:
- Throughout the procedure, an irrigation fluid is used to keep the surgical area clear.
- The interior of the bladder is carefully inspected to identify any remaining tumors or abnormalities.
Postoperative Catheterization:
- A catheter is often inserted into the bladder after the surgery to drain urine and allow the prostate and urinary tract to heal.
- The catheter may be connected to a drainage bag and is usually removed within a day after the procedure.
Recovery and Hospital Stay:
- Most patients can expect a same day discharge.
- Recovery time varies, but patients may experience some discomfort, urinary urgency, or blood in the urine initially.
Follow-Up:
- Patients will have follow-up appointments to monitor their recovery and address any concerns or symptoms.
- The healthcare provider will discuss postoperative care, including the resumption of normal activities and any restrictions.
Potential Benefits:
- TURP aims to relieve symptoms associated with BPH, such as frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urine flow, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
